Can you look at your phone while wearing polarized sunglasses?
That's because polarized lenses filter the light from some phones, leaving only black stripes visible.Polarized sunglasses have polarized lenses, and cell phone screens have polarized patches in their components. The polarized film has the function of shielding and passing through the incident light, which can make the longitudinal light or transverse light one kind of passing through, one kind of obscured. Because different phones have different polaroid settings, there will be different shades at different viewing angles. Thanks to a combination of polarizing lenses and lenses, both of which filter the direction of light, the screen can't be seen when the shielding and penetrating parts overlap.
Does blue light cause damage to the eyes?
Businesses often associate blue light with mobile phones and computers that everyone frequently touches. There are also many terrible explanations about blue light on the Internet, ranging from causing damage to the eyes to causing cancer. Therefore, in recent years, mass media and academic circles have caused heated discussions about the possible impact of blue light on eye health.
It is believed that the reason why blue light harms the eyes is that blue light is not like ultraviolet light which is absorbed by the cornea and lens so that it cannot reach the retina. Blue light can reach the retina through the refractive medium of the eye, and over time it will cause the aging and functional degradation of the retina. But in fact, the eyes have many protection mechanisms in the process of evolution, such as squinting, pupil contraction, lutein contained in the macula of the retina, the anti-oxidant repair mechanism of the retina, etc., which can protect our eyes from the damage of blue light. Also, after scientific testing, the blue light emitted by electronic products is a few percent of the intensity of blue light in natural light, which means that as long as the electronic products are not used continuously every day (for example, more than 8 hours a day), blue light will not be causes obvious damage to the eyes.
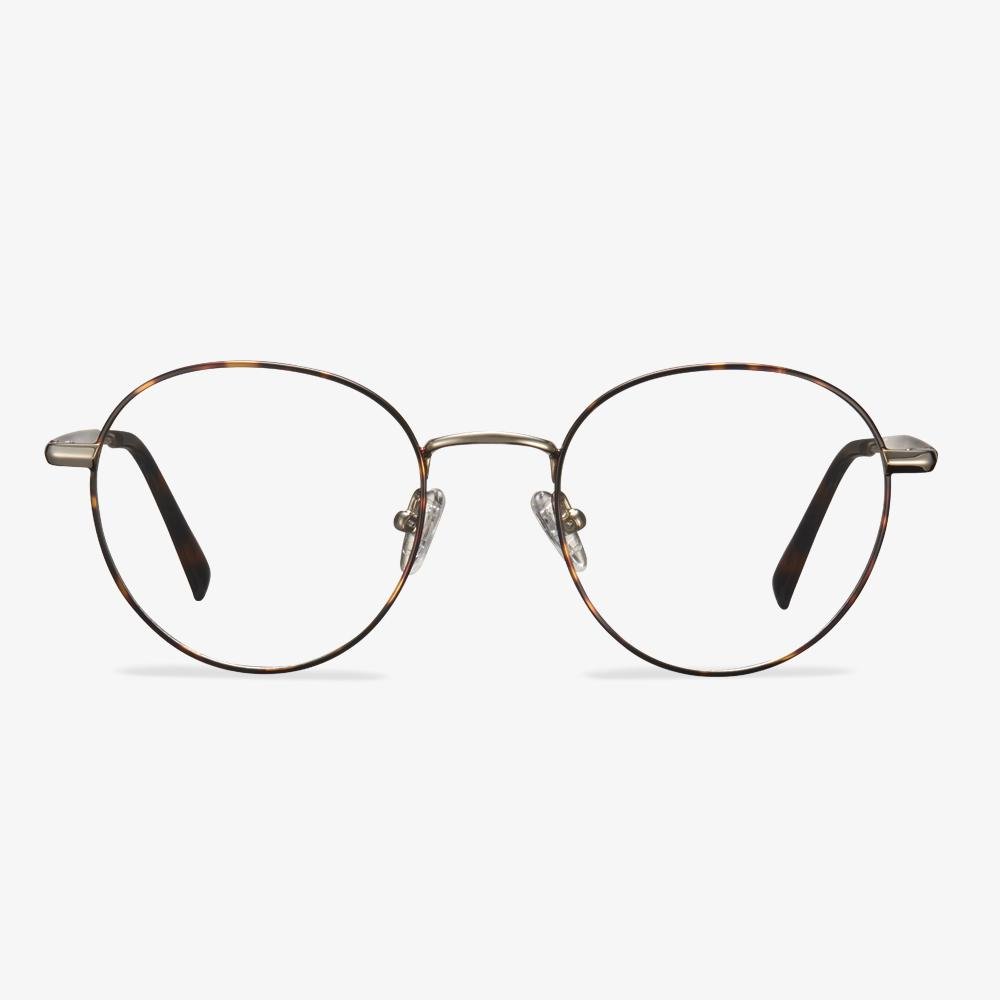
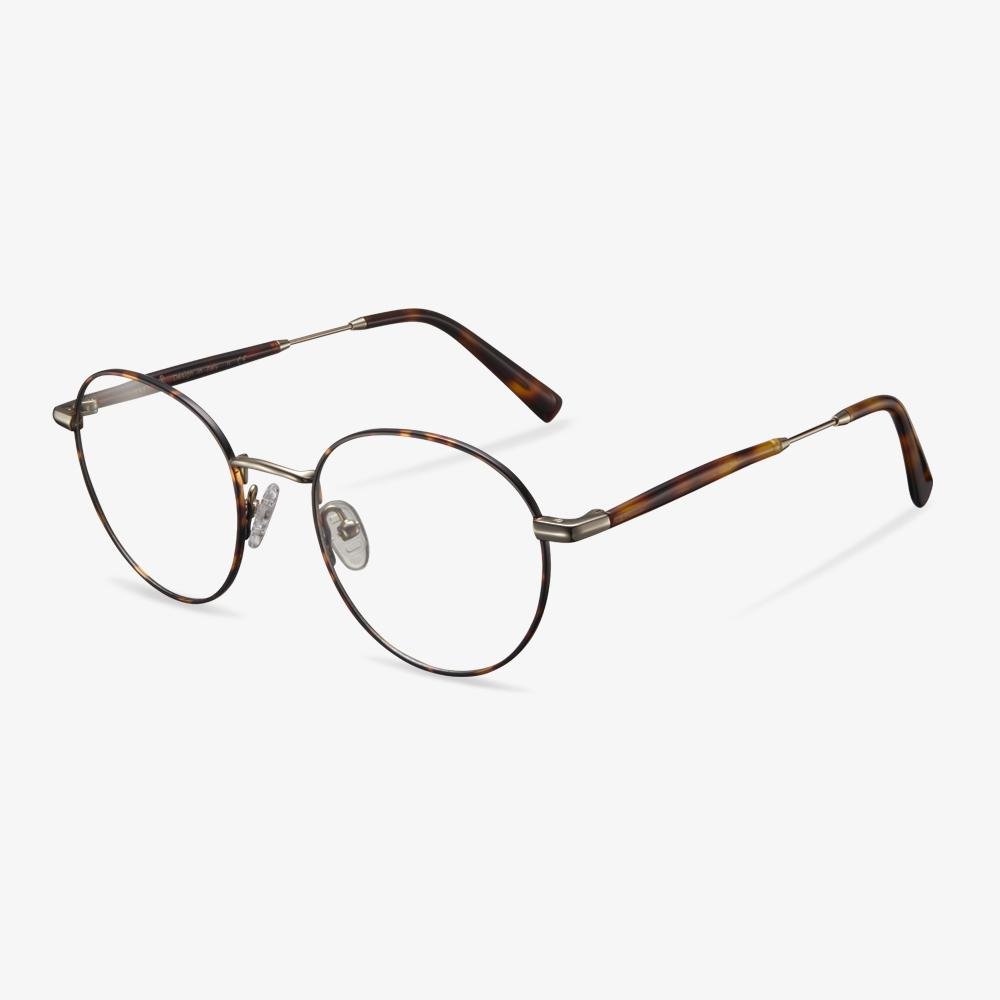
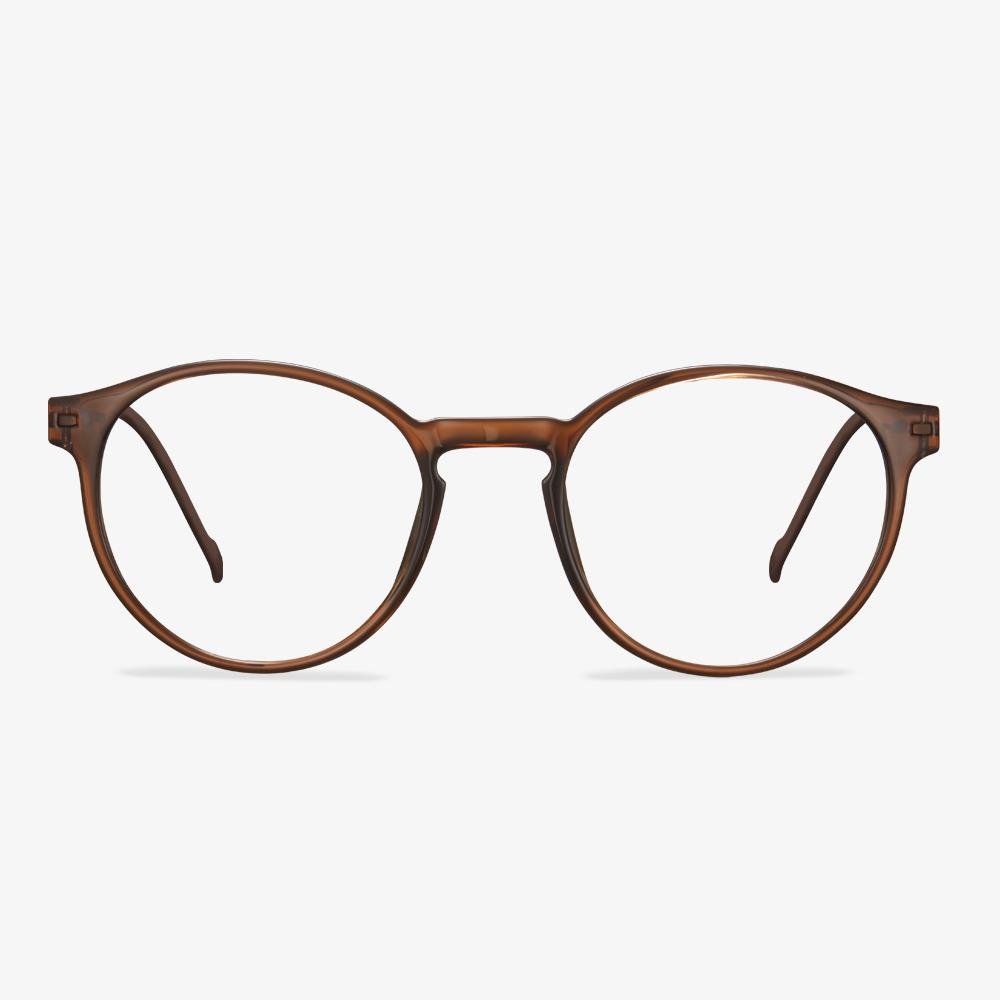
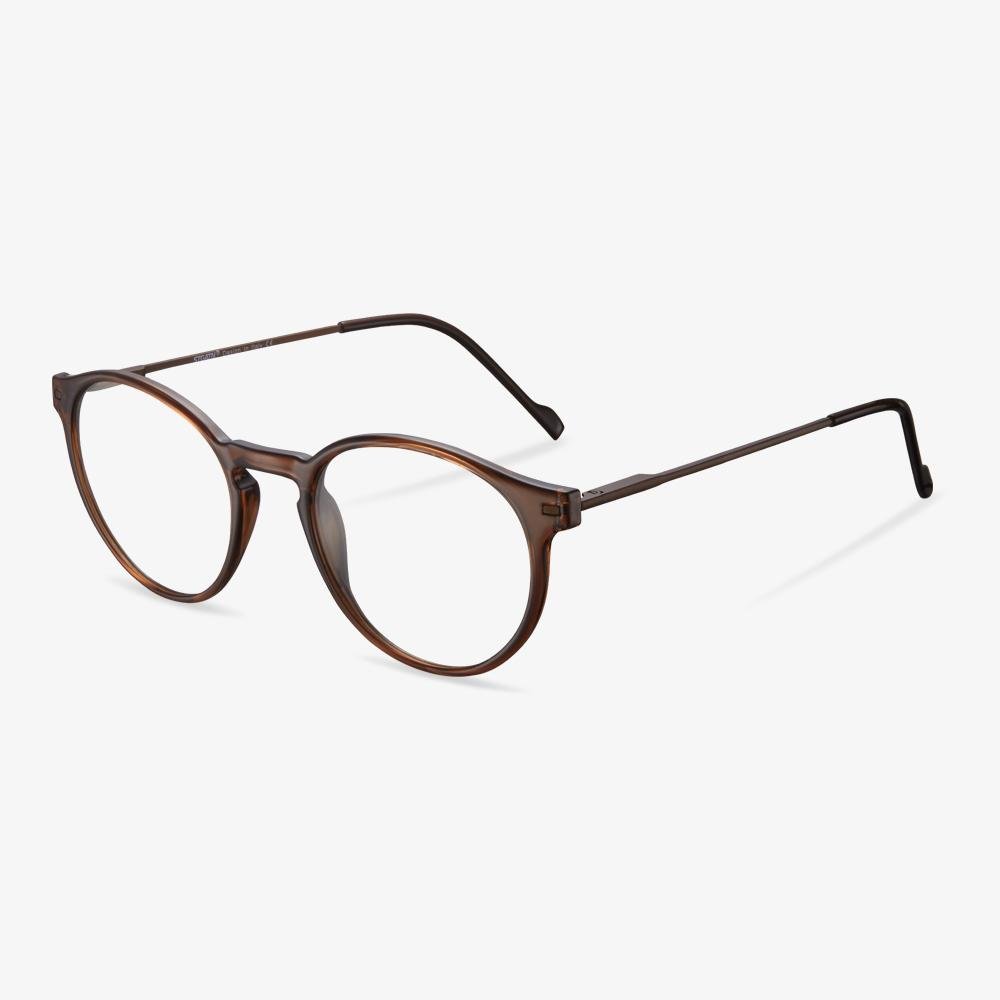
How Are Glasses Made?
In this section, we will show you how glasses are made. Here are a few steps.
- Eyeglasses lenses are first made by an optician reviewing your prescription and taking a lens bank that closest matches your prescription.
- The optician puts the lens bank into a grinding machine and grinds it into a shape that matches your prescription even closer.
- Then the glasses lenses are edged and cut into a shape that fits the frame you chose.
- Last, put the cut lenses into a solution so as to protect them from scratches, then give them a tint and more.
After all steps are finished, the glasses are made successfully.
The taboos of wearing glasses while driving at night
Night driving members should not wear tawny, green, and gray glasses. Tawny glasses can filter out most of the ultraviolet rays, although can make our eyes feel relaxed but easy to make people sleepy. Green glasses will turn red lights into black, directly affecting our judgment of traffic lights, so there is a great safety risk. Grey glasses, due to their low light transmittance, will weaken our line of sight and affect our observation of the road.
Are night driving glasses good?
The color of night driving glasses can be selected from yellow to amber. Yellow lenses will reduce the light entering the eyes and reduce visibility. At night, this can be harmful. The lens filters out a lot of glare, but also filters out other visible light, making it difficult to see objects in dim or dark conditions.
Some people who wear night driving glasses say that they are more capable of seeing things at night. However, related test studies have shown that driving glasses at night does not improve night vision, nor can it help drivers see pedestrians faster than when they are not wearing glasses. A small study in 2019 showed that night driving glasses actually slow down the visual reflex by a fraction of a second, making night vision worse. So don't try to improve the safety of driving at night by wearing driving glasses with this kind of yellow lenses.
Does wearing sunglasses at night help driving? Like night driving glasses, sunglasses will reduce the amount of light entering the eyes, which makes them unsuitable for night driving and potentially dangerous.
Is blue light blocking worth it?
There are two main problems with anti-blue glasses currently on the market. One is that the place to be prevented is not preventable, and the other is that people have color casts due to wrong protection and aggravate visual fatigue. Studies have shown that our eyes are the most intolerant of blue light in the 400-440 nanometer band. Therefore, current manufacturers mainly block blue light in this band when producing anti-blue glasses. However, the blue waveband of electronic products is between 450 nanometers and 490 nanometers, so most anti-blue glasses have little protection in this waveband. In addition, the blocking rate of anti-blue glasses is 20%~30% to achieve a good anti-blue light effect, but now the blocking rate of anti-blue glasses on the market has basically reached 80%~90%. All in all, these blocking blue light glasses cannot prevent the blue light in the 450-490 nanometer band, and their high blocking rate will also cause a color shift, which makes people more likely to have eye fatigue and headache.
In daily life, the intensity of blue light is low, not enough to cause damage to the fundus, so ordinary people do not need to wear anti-blue glasses unless they are working in extremely strong light conditions or working in special environments. To protect the eyes, it is more important for people to develop good eye habits. For example, wear a pair of suitable glasses and read insufficient light and at an appropriate distance. Avoid using electronic products for a long time. Take a break for 20 to 30 seconds every 20 to 30 minutes, and look at the distance regularly. If you have dry eyes while reading the electronic screen, remember to blink to 12 times per minute. It is best to wear sunglasses when outdoors.
Who need progressive lenses?
There is no limit to the degree of progressive multifocal lenses. Whether it is nearsightedness, presbyopia or moderate astigmatism, it can be worn, but not everyone can wear it. There are two types of progressive multifocal lenses on the market, one is hard and the other is soft. The main difference between the two designs is the length of the progressive channel. The rigidly designed progressive film has a short progressive path and relatively less peripheral aberrations. In order to ensure vision at various distances, fewer vertical dimensions are required. For example, a teenage progressive film belongs to this design, but because of its short gradual path, the gradation process is too short. Fast. Compared with the elderly, this design is more difficult to adapt; the soft design of the progressive film has a relatively long gradation channel and relatively large peripheral aberrations, but due to its long gradation channel, the gradation process is relatively smooth, which makes it easy to wear glasses It is suitable for people with poor adaptability.
If you are a person who is able and willing to accept new things, understand and adapt to the temporary discomfort caused by progressive addition lenses, we suggest that he can wear a pair, if he has severe hypertension, dizziness and other symptoms, or People who have misunderstandings about progressive lenses and are unwilling to adapt should not try them. Because you first wear progressive multifocal glasses, you may experience: slight dizziness, shaking when walking, and being careful when moving up the stairs.
The perception of space has changed, the perception of the distance of the object, and the perception of depth have changed. New wearers should not drive immediately and do strenuous exercise. When you look close, you need to turn your eyes down, and your eyes are mildly uncomfortable. Seeing an object through the blurred vision area around the lens makes the object blurred. Therefore, when new wearers look at things, turn their heads more, turn their eyes less, try to use the far-use zone, the near-use zone, and the middle-distance zone to see objects.