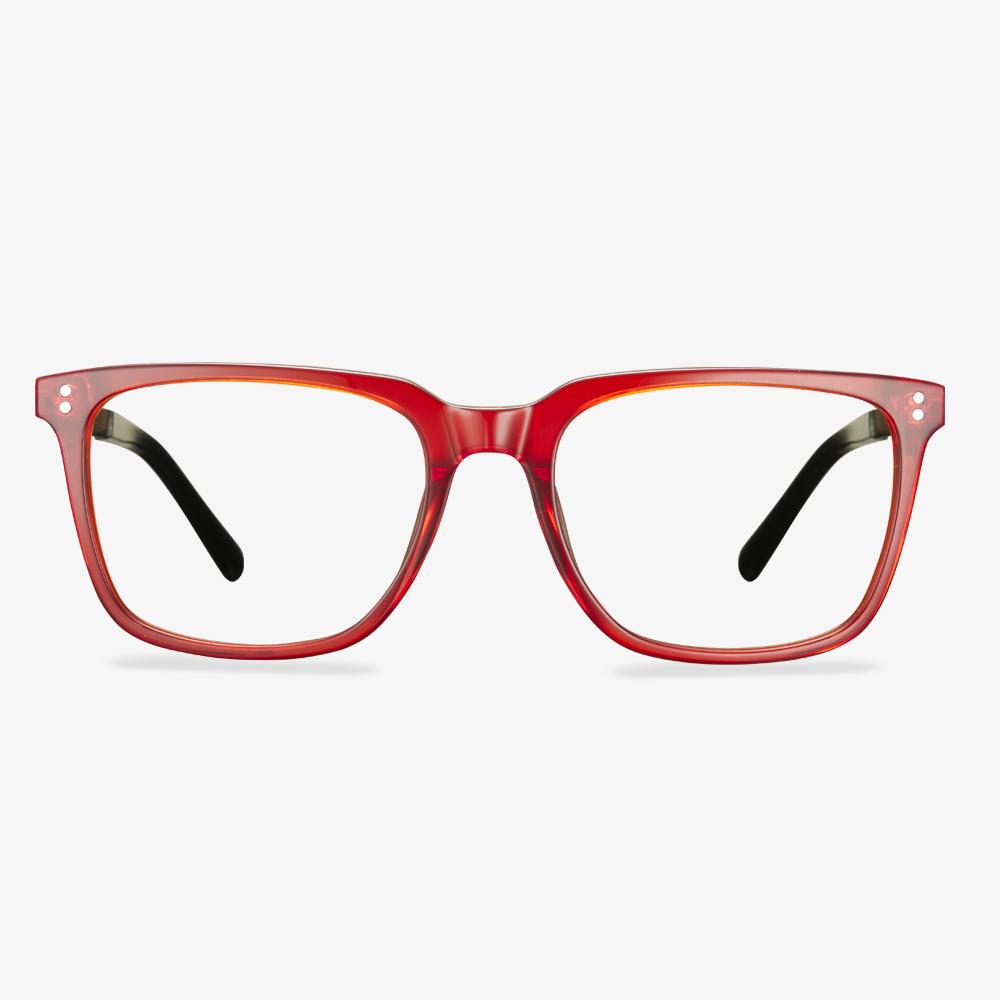
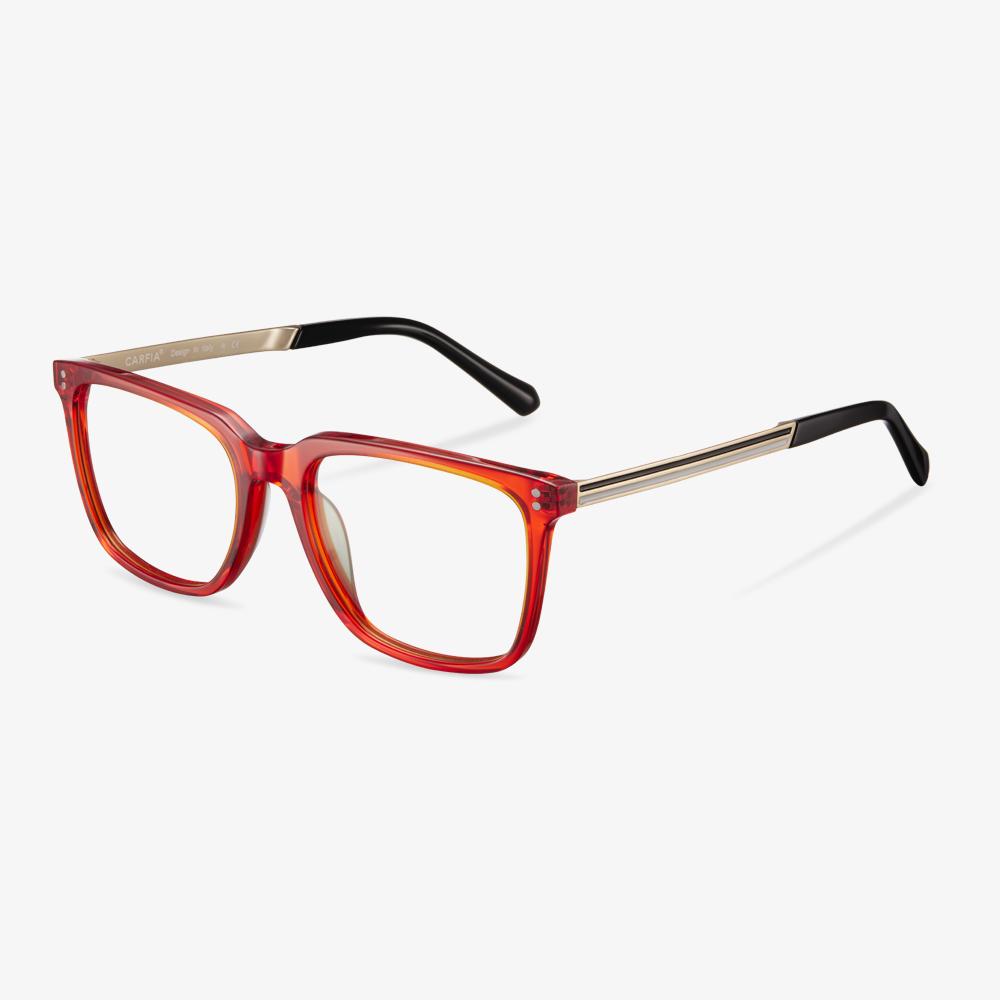
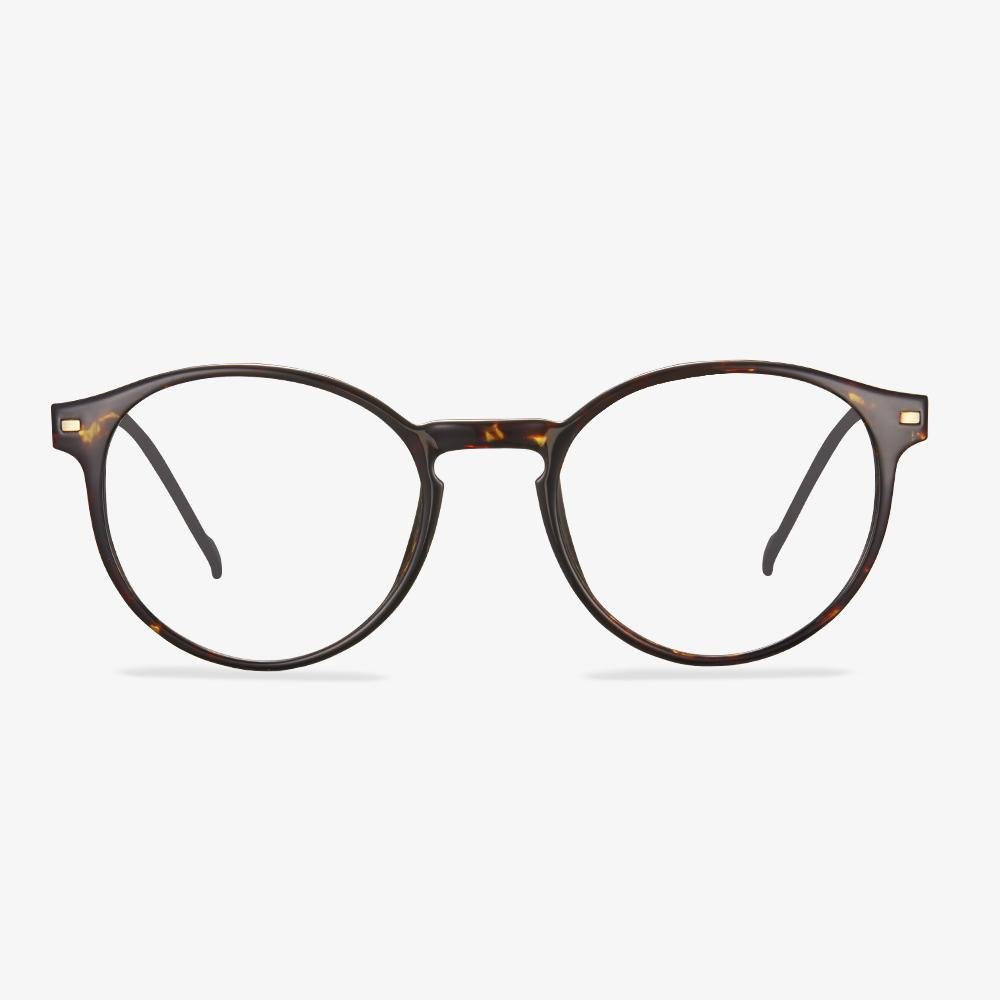
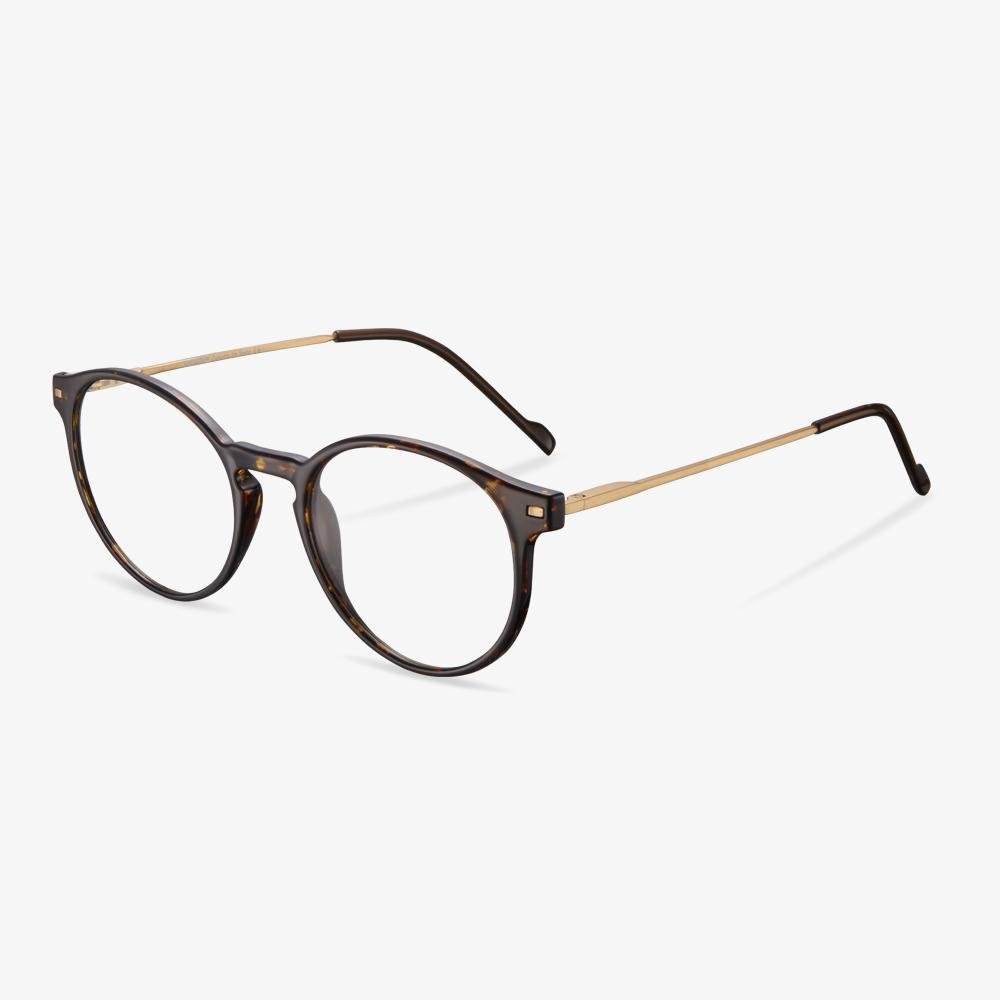
Do you need to wear glasses to drive?
In the evening, lights from street lamps, buildings, and other vehicles create a lot of reflection on the windshield, making it hard to see. It's even worse when it rains. But if your glasses have an anti-reflective coating, they can reduce the glare and reflections, allowing you to see more clearly while driving at night.
What Is Anti Reflective Coating?
Anti reflective coating, also known as AR, anti-glare, no-glare, or glare-free coating, can provide benefits to your vision. Anti reflective coating is added to lenses to reduce glare caused by light hitting the back of the lenses to improve your vision and make your eyeglasses more visually attractive.
Anti reflective coating will eliminate all reflections from the front and back surfaces of your lenses. Hence, more light is able to pass through your lenses which improves your vision. At the same time, fewer distractions are visible and the lenses are hardly noticeable, especially in the dark. So, is anti glare worth it? Most people agree that.
Understand blue light correctly.
Blue light has been shown to affect the body's circadian rhythms, with too much exposure to it late at night from gadgets such as mobile phones disrupting a person's ability to fall asleep. Therefore, it is recommended that people limit screen time two to three hours before bedtime and set their devices to night mode to reduce glare, relieve eye fatigue and minimize blue light at night. However, as we learn more about blue light, not all of it is bad for us. Blue light has been found to play an important role in maintaining health, such as regulating the secretion of hormones in living organisms. Blue light helps prevent reduced night vision and has been shown to benefit refractive development in adolescents and minors.
How Long Does It Take to Get Used to New Glasses?
Most people are excited when they get a new pair of glasses for the first time. But sometimes there is an adjustment period before your vision is fully comfortable. So, how long does it take to get used to new glasses?
In most cases, it takes only a few days to adjust to a new pair of glasses. When you are adjusting to your new glasses, you might experience some symptoms such as mild dizziness, blurry vision, or eye strain. This would be a normal situation. These symptoms are common with new glasses and typically last only a few days.
Even though the new glasses come with the same prescription, different frames or lenses can alter your vision until you get used to the new frame style, frame material or lens type.
Besides, other factors will affect the adjustment time, such as the complexity of your prescription, the type of lens, and so on.
How long does it take to adjust to new glasses? It usually takes a few days. However, if you experience eye strain, distorted vision, and especially headaches for a few weeks, you had better contact the eye doctor or the optician. They will check your eyeglass and the prescription.
Liingo Eyewear
Find the 5 frames you dug. Try it for 5 days. Spend some time with your new frames to see which ones are right for you. With home trials, you can try on up to five pairs at a time. And if that's not enough, with their virtual try-on service, you can try on any frame you want right away. Put all five frames back in the box, tear off the current shipping label to reveal the pre-paid return label.
Can clear lenses be polarized?
At present, there are no clear polarized lenses. A polarized lens is a thin film vertically arranged with silicon crystal coating placed inside the lens, just like a shutter, which covers the parallel light and only allows the vertical light to pass through. In this way, the glare from all directions can be eliminated, so it is clear and comfortable to wear. Transparent polyamide, the material of nylon lens, is a new variety of polyamide. The material of the nylon lens is mainly transparent polyamide. Due to the effect of the light filter, only light from a specific direction is allowed to pass through the lens, which filters the dazzling light from the sun on the water, land, or snow very well. It can not only make the landscape soft, clear, and natural but protect the eyes to a certain extent.
Who need progressive lenses?
There is no limit to the degree of progressive multifocal lenses. Whether it is nearsightedness, presbyopia or moderate astigmatism, it can be worn, but not everyone can wear it. There are two types of progressive multifocal lenses on the market, one is hard and the other is soft. The main difference between the two designs is the length of the progressive channel. The rigidly designed progressive film has a short progressive path and relatively less peripheral aberrations. In order to ensure vision at various distances, fewer vertical dimensions are required. For example, a teenage progressive film belongs to this design, but because of its short gradual path, the gradation process is too short. Fast. Compared with the elderly, this design is more difficult to adapt; the soft design of the progressive film has a relatively long gradation channel and relatively large peripheral aberrations, but due to its long gradation channel, the gradation process is relatively smooth, which makes it easy to wear glasses It is suitable for people with poor adaptability.
If you are a person who is able and willing to accept new things, understand and adapt to the temporary discomfort caused by progressive addition lenses, we suggest that he can wear a pair, if he has severe hypertension, dizziness and other symptoms, or People who have misunderstandings about progressive lenses and are unwilling to adapt should not try them. Because you first wear progressive multifocal glasses, you may experience: slight dizziness, shaking when walking, and being careful when moving up the stairs.
The perception of space has changed, the perception of the distance of the object, and the perception of depth have changed. New wearers should not drive immediately and do strenuous exercise. When you look close, you need to turn your eyes down, and your eyes are mildly uncomfortable. Seeing an object through the blurred vision area around the lens makes the object blurred. Therefore, when new wearers look at things, turn their heads more, turn their eyes less, try to use the far-use zone, the near-use zone, and the middle-distance zone to see objects.