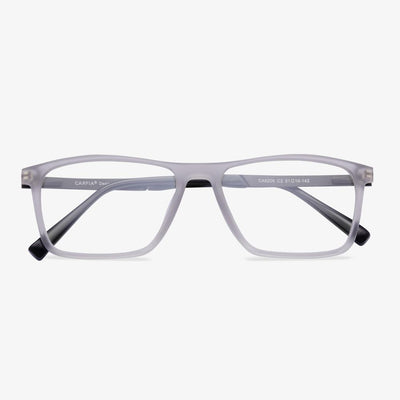
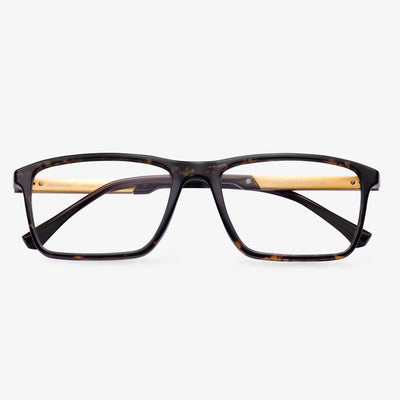
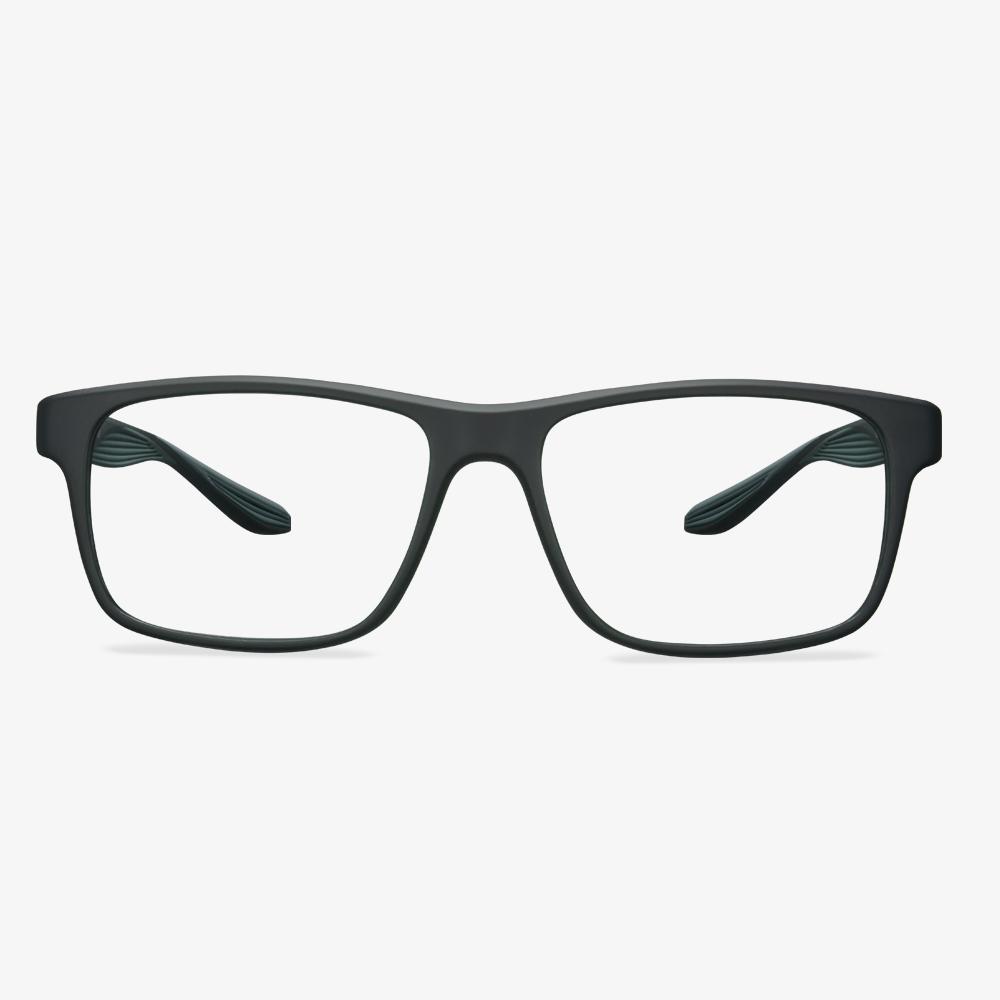
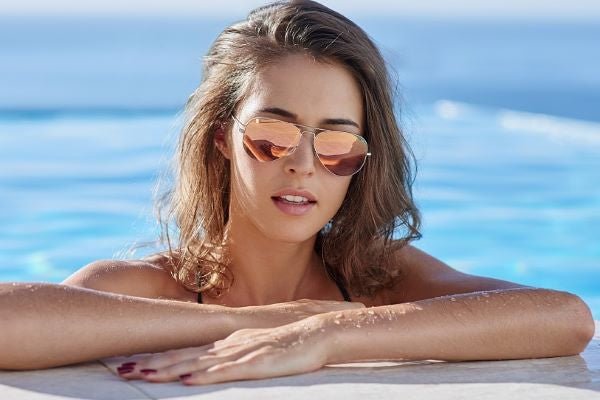
How do you identify the refractive index of lens?
In reality, this problem is often a problem for optical shop practitioners, sometimes they worry about whether the manufacturer's lenses match the nominal value of the refractive index. We need a prop, and that's the camber. Because it can be used to measure the strength of the lens. The luminosity of the lens can be calculated by subtracting the curvature of the inner and outer surfaces of the lens. The curvature difference of a lens of the same luminosity is inversely proportional to the refractive index, that is, a lens with a higher refractive index only needs a smaller curvature difference to achieve the same luminosity.
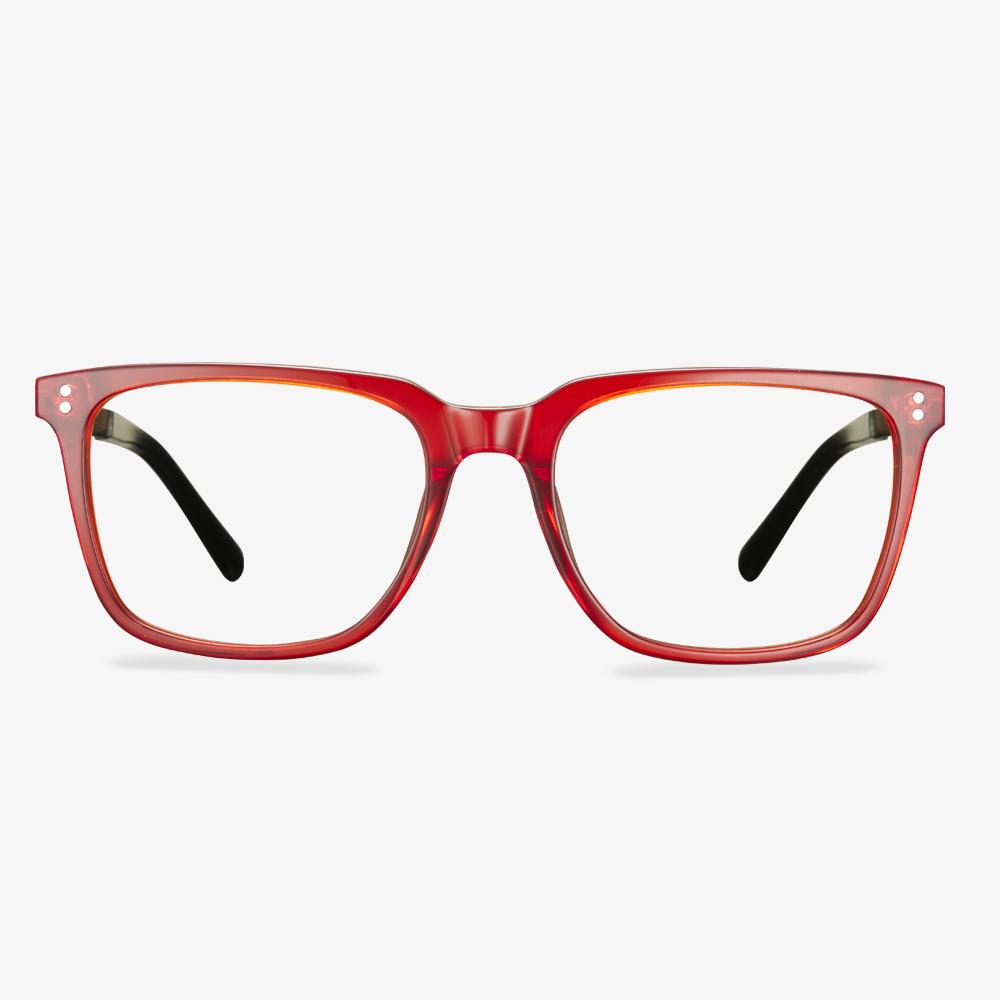
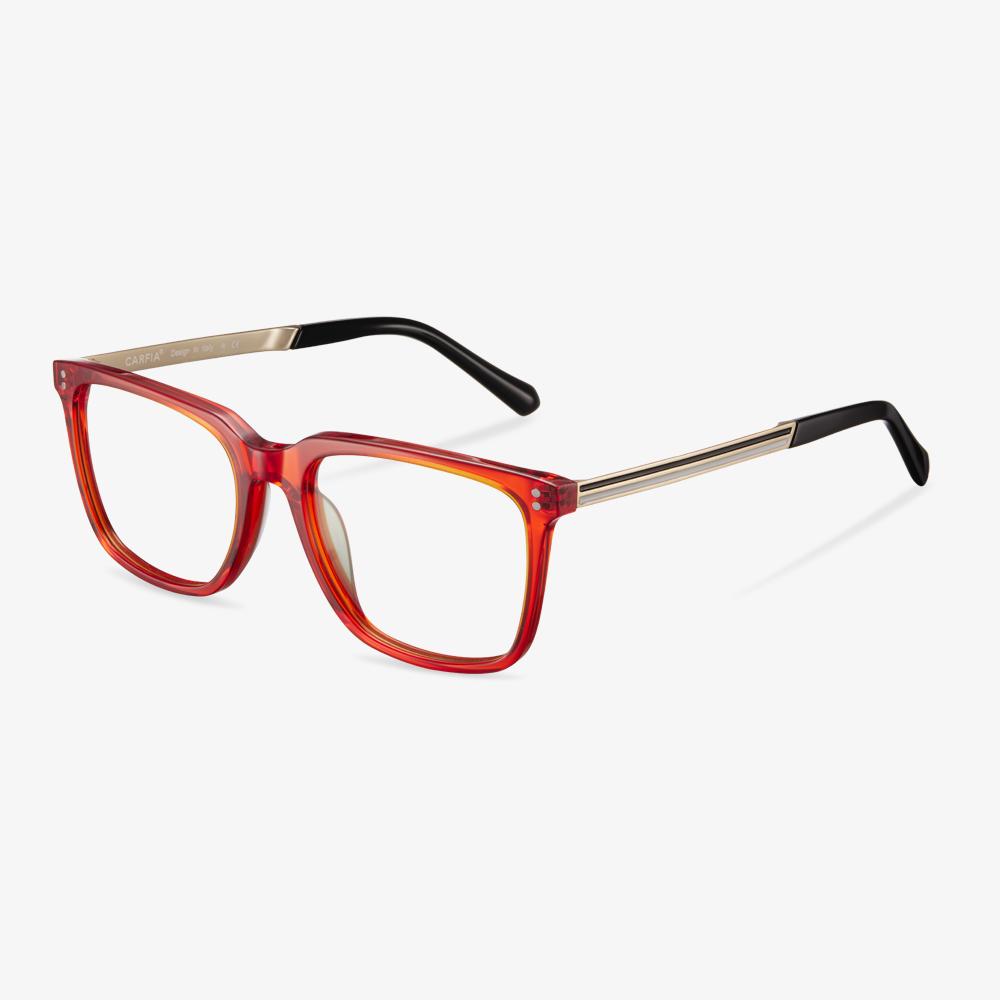
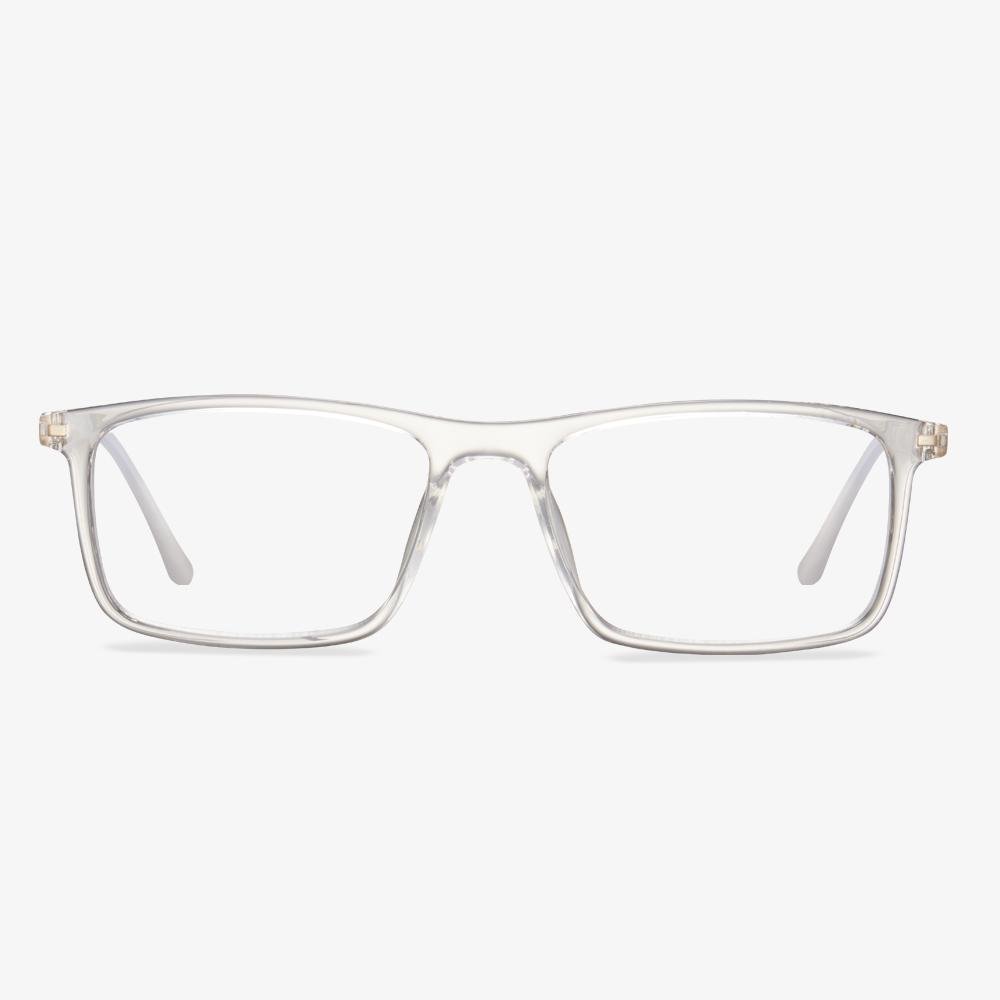
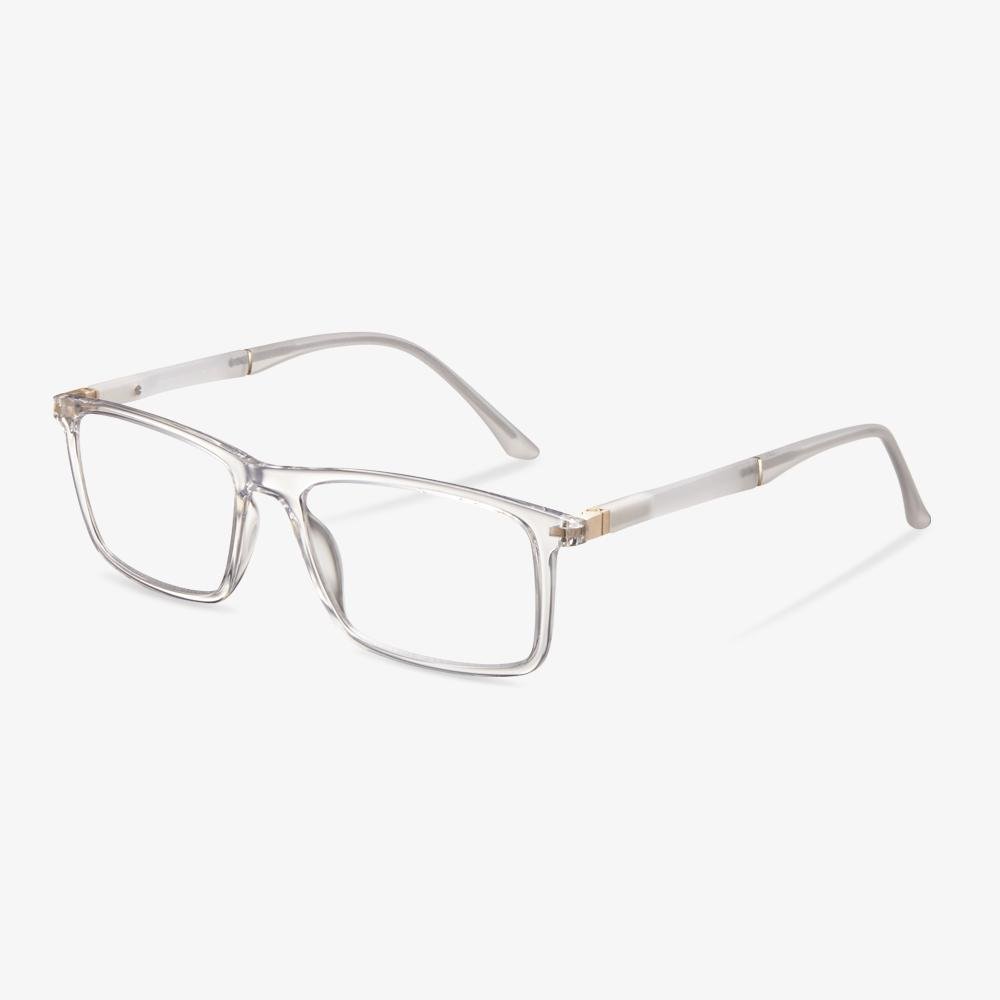
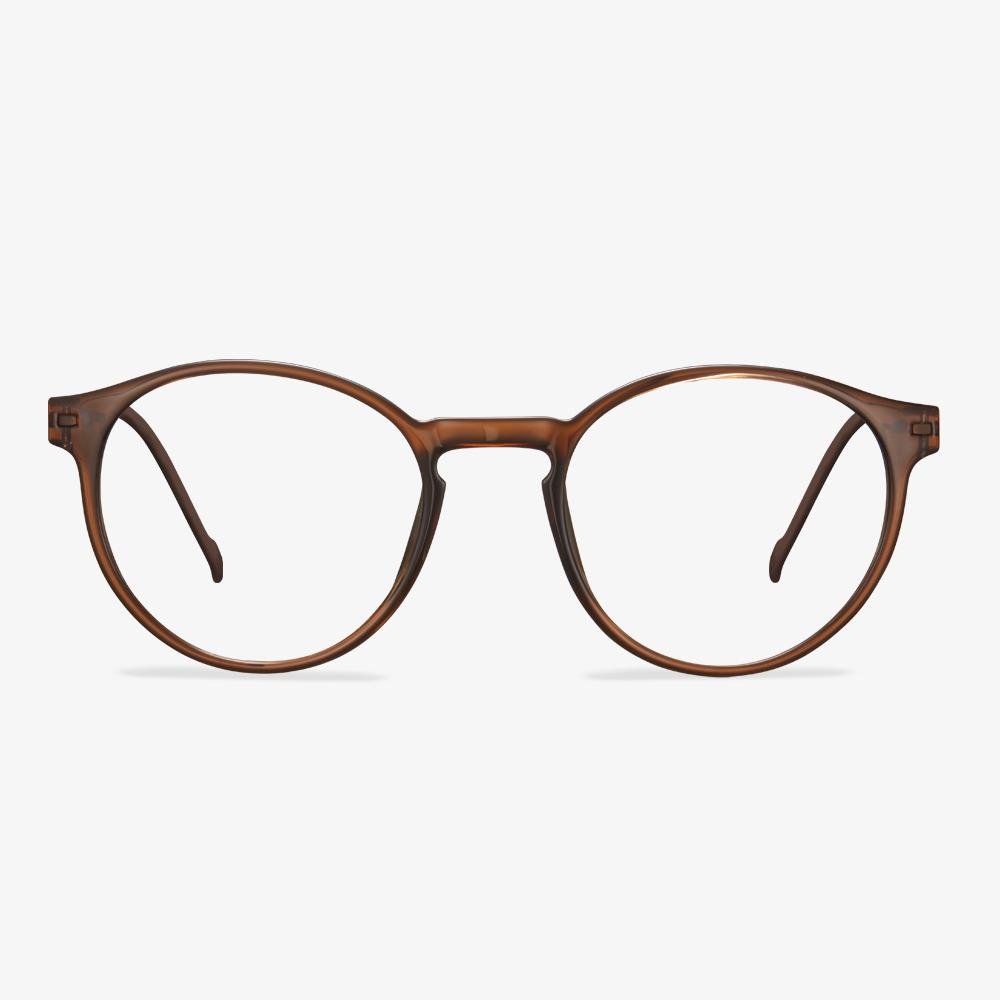
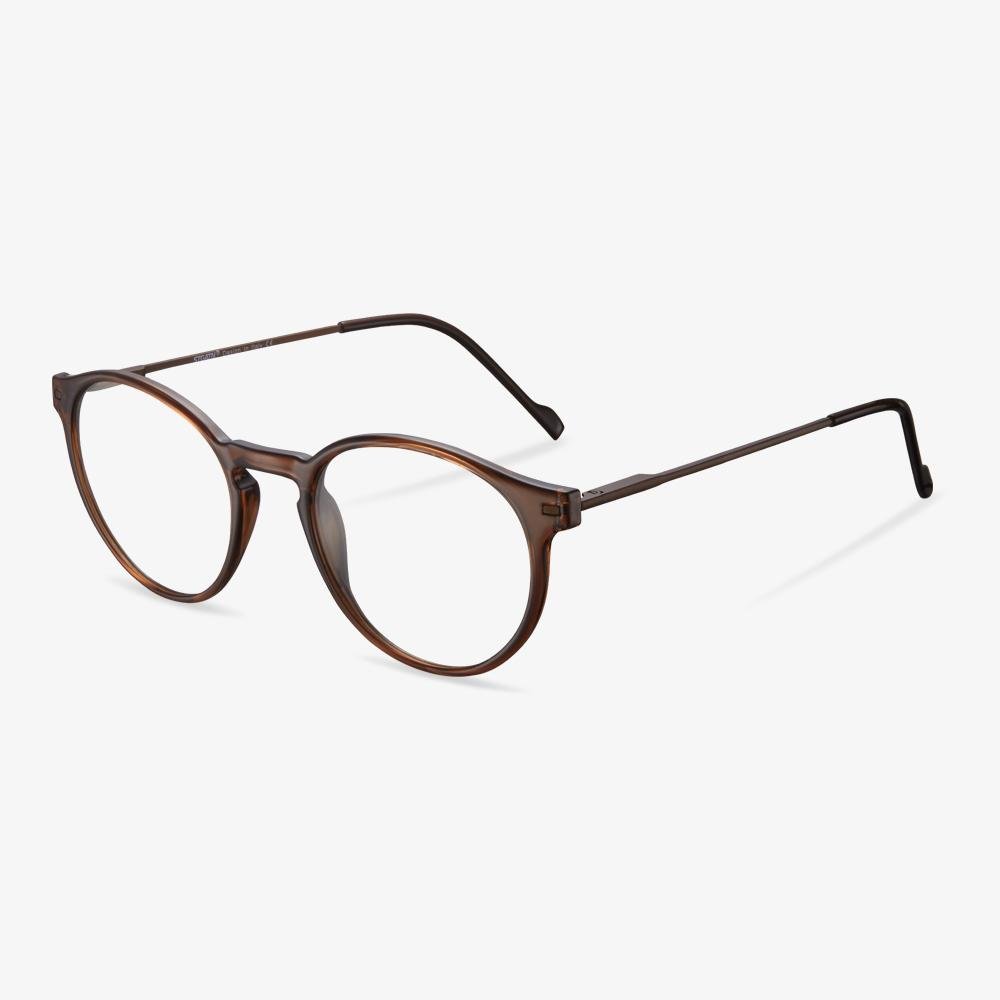
Retro glasses
The retro glasses have a strong retro flavor. Then, of course, you should choose a special design to wear, simple will make you stand out from the crowd. The square full frame is very retro, using special metal. The metal frame wears comfortable and has a better decorative effect.
The design evolution of progressive lenses
Spherical and aspheric designs
The design of the front surface of the far-use area of the early progressive lens is similar to that of the ordinary spherical single vision lenses, so it is called a spherical progressive lens. Since 1974, the front surface of the far-use region of the lens is designed to be aspheric by designers, which not only reduces the peripheral aberration but makes the lens thinner, lighter, and less powerful.
Hard and soft design
For hard design, the channel is short, and the gradient is large. The near-use area position is high. The effective visual area of remote and near-use areas was larger. Peripheral astigmatism is relatively concentrated. Because surrounding astigmatism increases rapidly and the distribution is dense, the curve effect is more obvious. The gradient area is narrow. It is more difficult and takes longer for wearers to adapt.
Lenses with soft designs have slower gradients, longer gradients, and wider gradients. The angle of rotation of the eye from the far area to the near area is greater. It's easier to get used to. Compared with the hard design, the effective visual area of the far and near use areas is smaller, and the location of the near use area is lower.
Single, diverse, and individualized design
Initially, the progressive lenses used a single design, in which each basic curve was scaled equally and a luminosity combination was added within the range of its semi-finished lens blanks. The steepest base curve uses the same lens design as the flattest base curve. Lenses designers quickly realized that the overall performance of the lens could be improved by microcustomizing the lens design, leading to progressive lenses with multiple designs. This kind of design is called diverse design. By the mid-1990s, there was the emergence of individualized lens designs. In addition to using different gradients, these first individualized lens designs used steeper baseline curves with a slightly larger approach area to compensate for increased magnification and reduced field of view.
Symmetrical and asymmetric design
There is no difference between the left and right eyes in the symmetrical design of progressive lenses. As the eyes turn inward when they see near objects, the gradual gradient area gradually tilts to the nasal side from top to bottom, so the left/right progressive lenses should be rotated clockwise/counterclockwise respectively during processing. An asymptotic lens with left and right eye divisions is called an asymmetric design. The gradient is gradually and moderately inclined to the nasal side from top to bottom. The refractive force, astigmatism, and vertical prism of the two sides of the left and right gradient of the asymmetric design lenses are basically similar. At the same time, considering the characteristics of eye movement parameters in binocular vision, the peripheral aberrations of the corresponding positions of the left and right lenses were appropriately balanced to improve the visual effect of the wearer.
How to Choose Reading Glasses?
Choose big frames the first time. When choosing reading glasses, you can choose the big frames for the first time. You may need larger glasses frames or lenses to really get the sweet spot of where the prescription is.
And if you have never worn glasses for eye conditions such as nearsightedness, farsightedness or astigmatism, it is likely you will be able to see well with non-prescription reading glasses. So, you can buy these non-prescription reading glasses.
Fetch Eyewear
With so many styles to choose from, trying on frames from the comfort of your home can help narrow your search for new prescription glasses. The Home Try On program makes it easy. Because all non-prescription glasses (including sunglasses and readers) are 100% returnable. The Home Try-On program will focus on customers who buy prescription glasses. Send the prescription to the appropriate email or upload it at checkout. After completing the $0.99 temporary licensing fee, your Try At Home kit is complete. This fee will be refunded to your card once they receive your kit.
Points To Note When Choosing Frames
Choose a frame with lightweight, good elasticity, and stable structure. The lens frame with poor quality tends to deform in use, which affects the optical properties of the glasses. Pay attention to whether the two sides of the frame are symmetrical and whether it is fixed and safe enough. Pay attention to whether there are scratches on the surface of the frame. Just put on the glasses to feel if it is very tight or very loose, and they must be tight to reach the saturation condition. Pay attention to distinguish the advantages and disadvantages of the coating. The better coating frame has a uniform color, smooth surface, and clear identification. After using the frame with poor coating quality, the frame will soon rust and fall off, affecting the life of the frame, and even causing skin discomfort or allergy.
How to drive at night with glasses?
Far-light is easy to cause blind spots for drivers of opposite vehicles, and it is possible to cause traffic accidents when driving in the cities. In the process of driving, if the driver encounters the situation that a high beam disrupts the line of sight, can turn the eye in the left or right direction, avoid light sources, and allow your eyes to gradually adapt to the other person's light source. If you can't see clearly, slow down or even pull over.