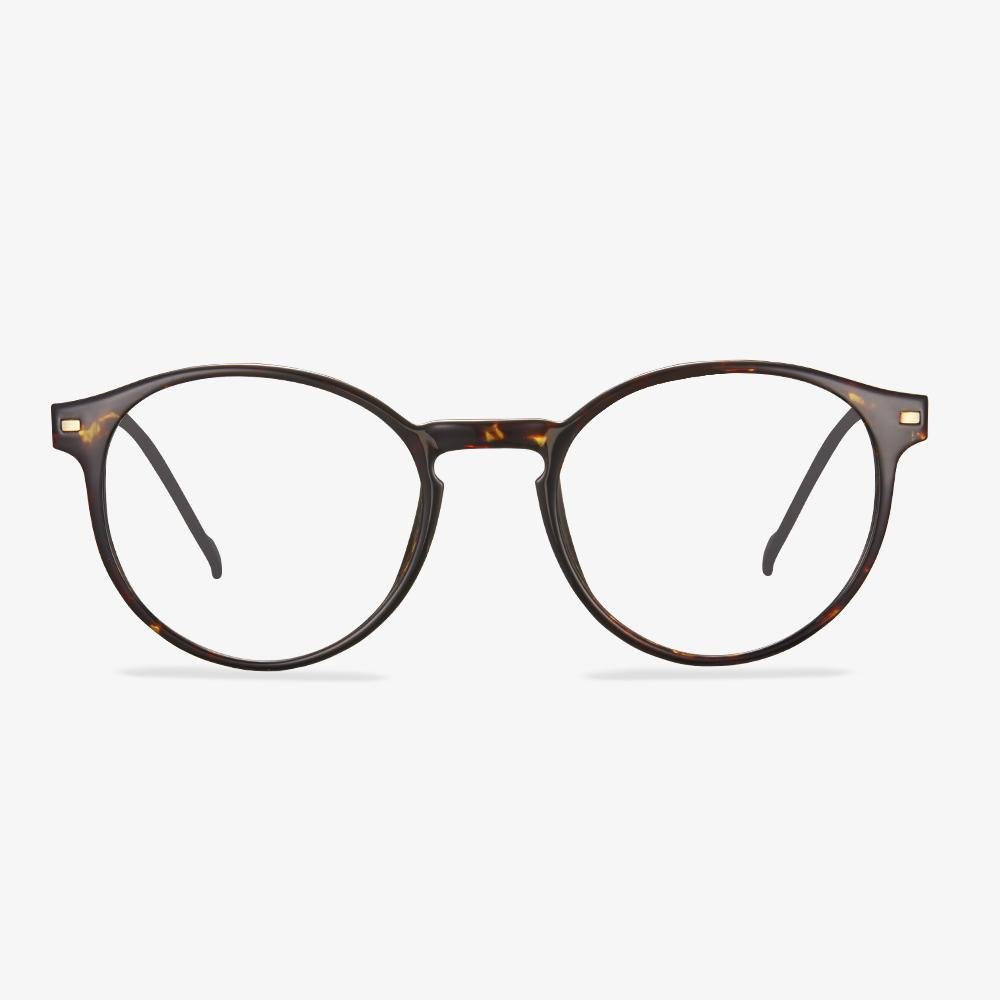
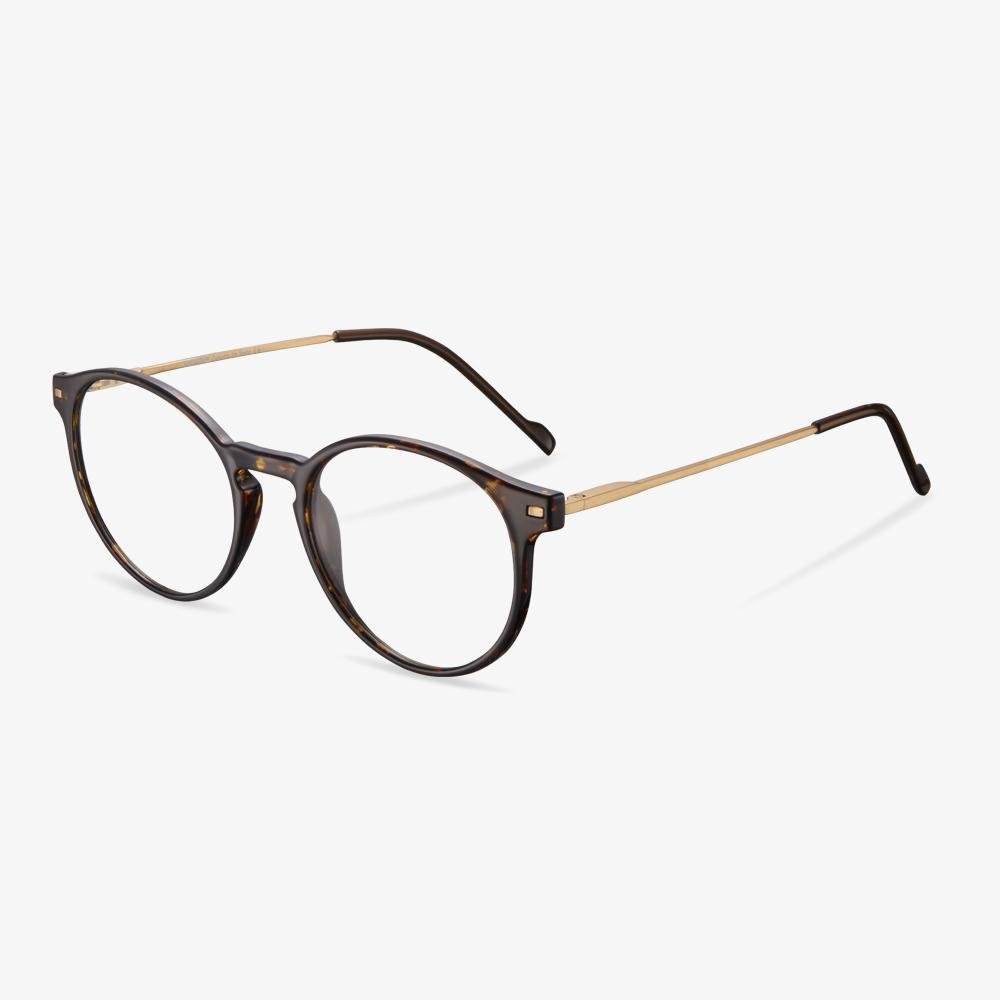
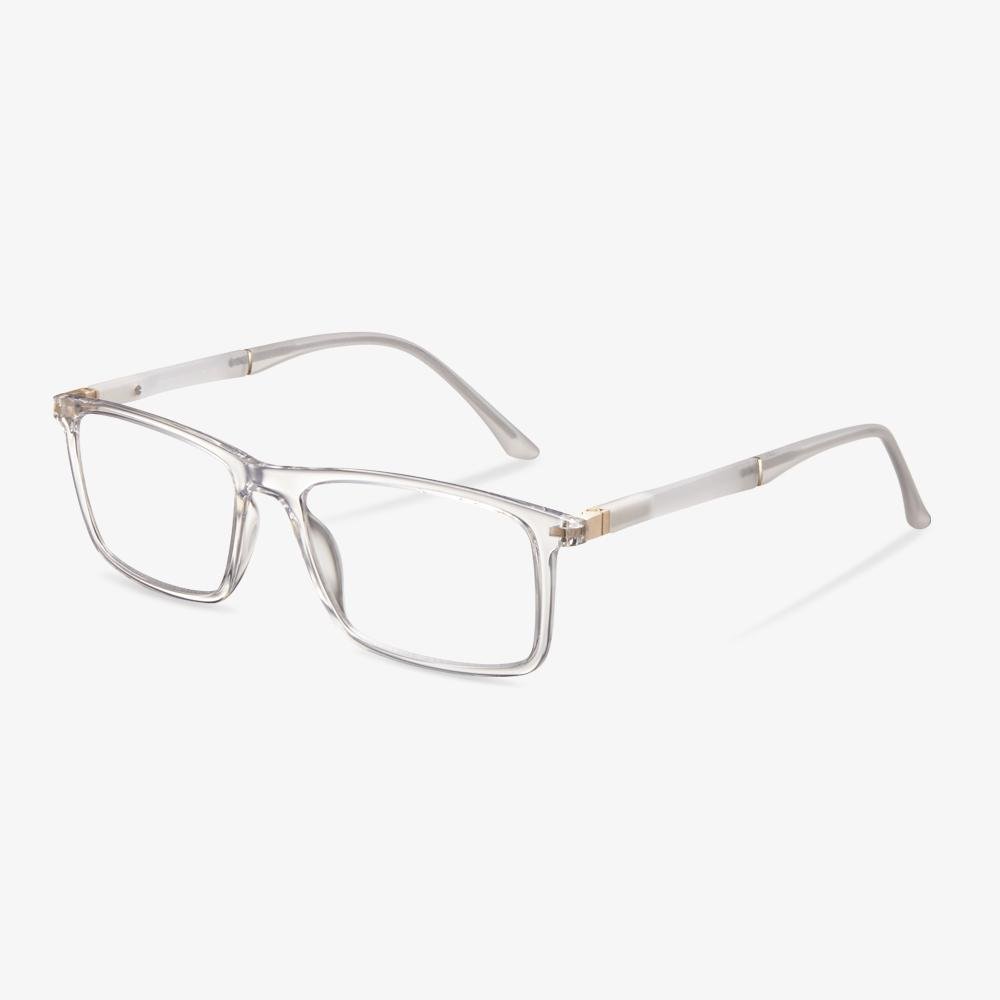
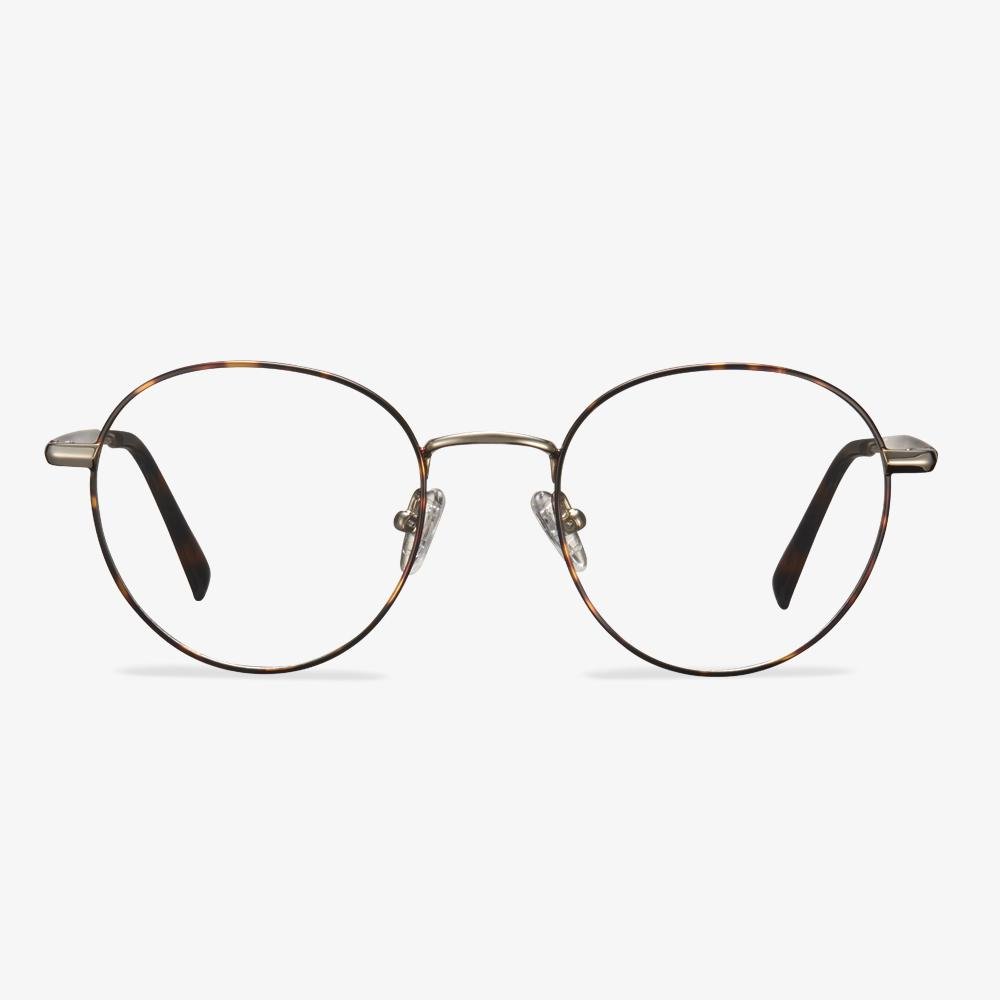
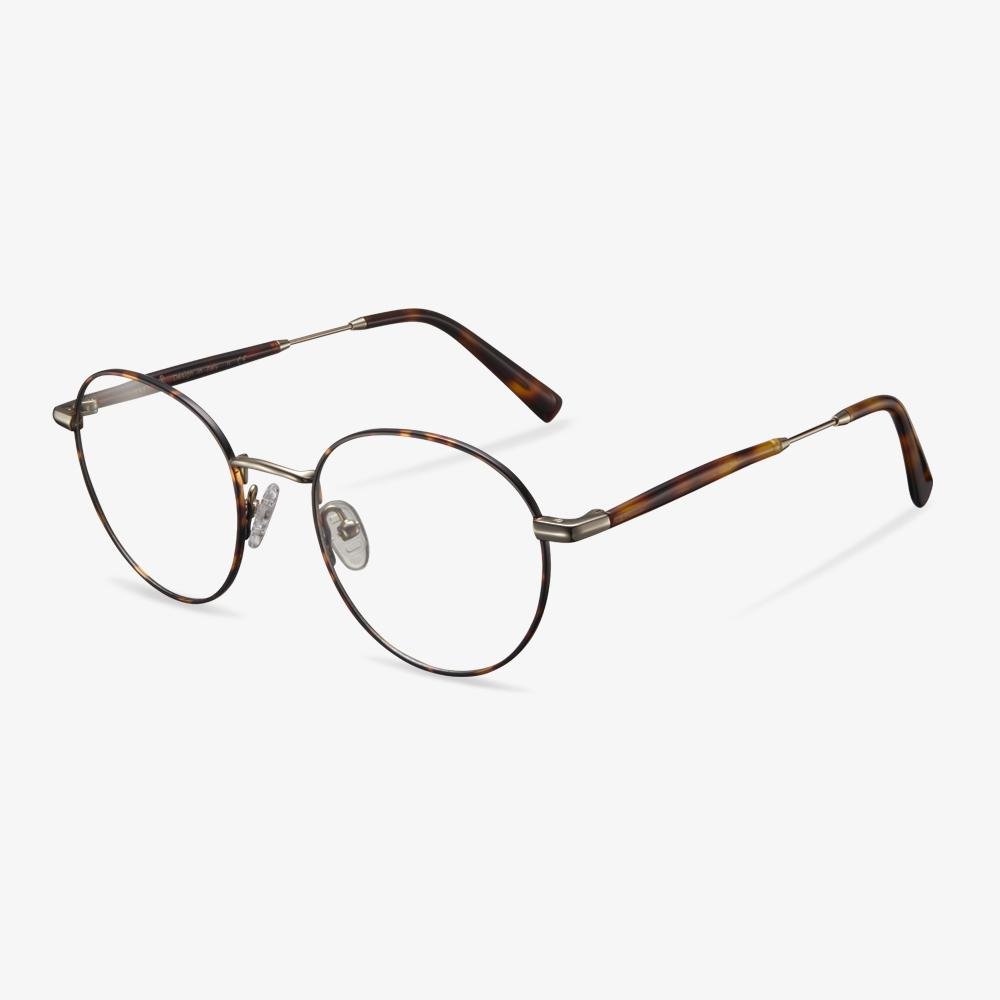
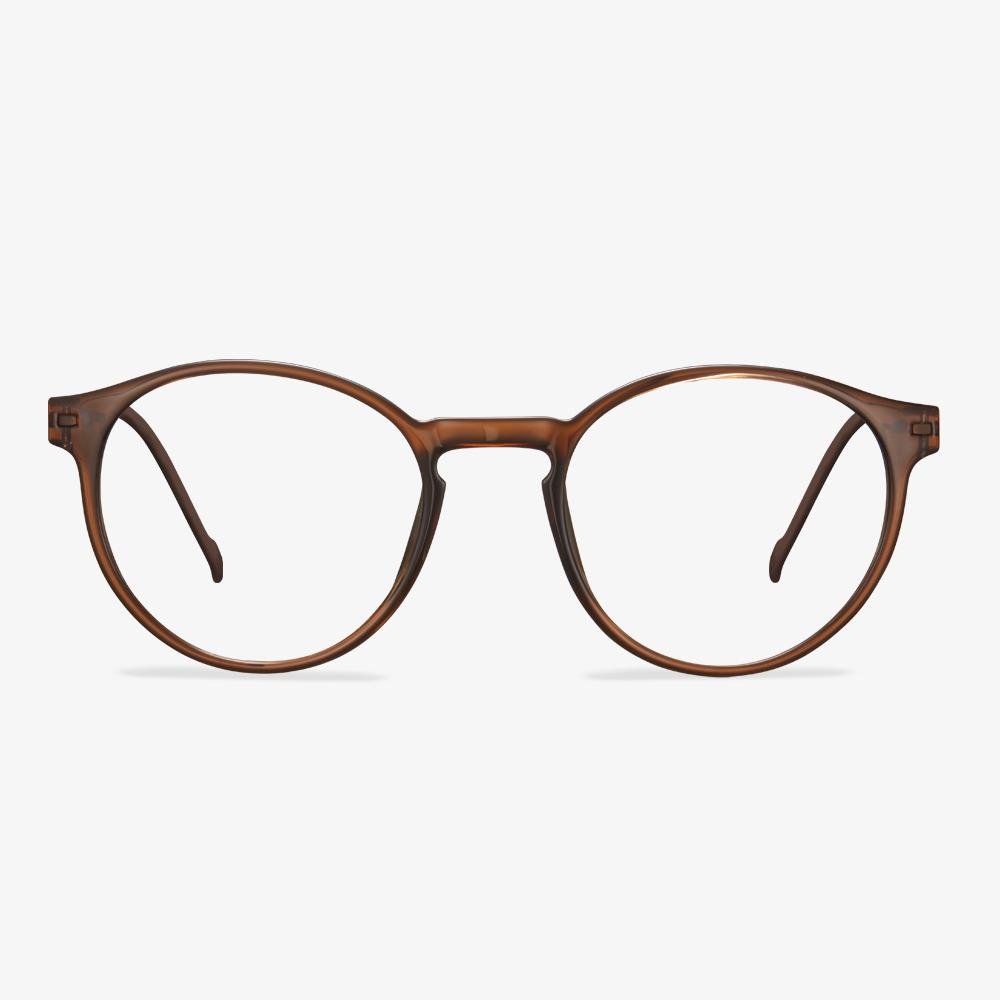
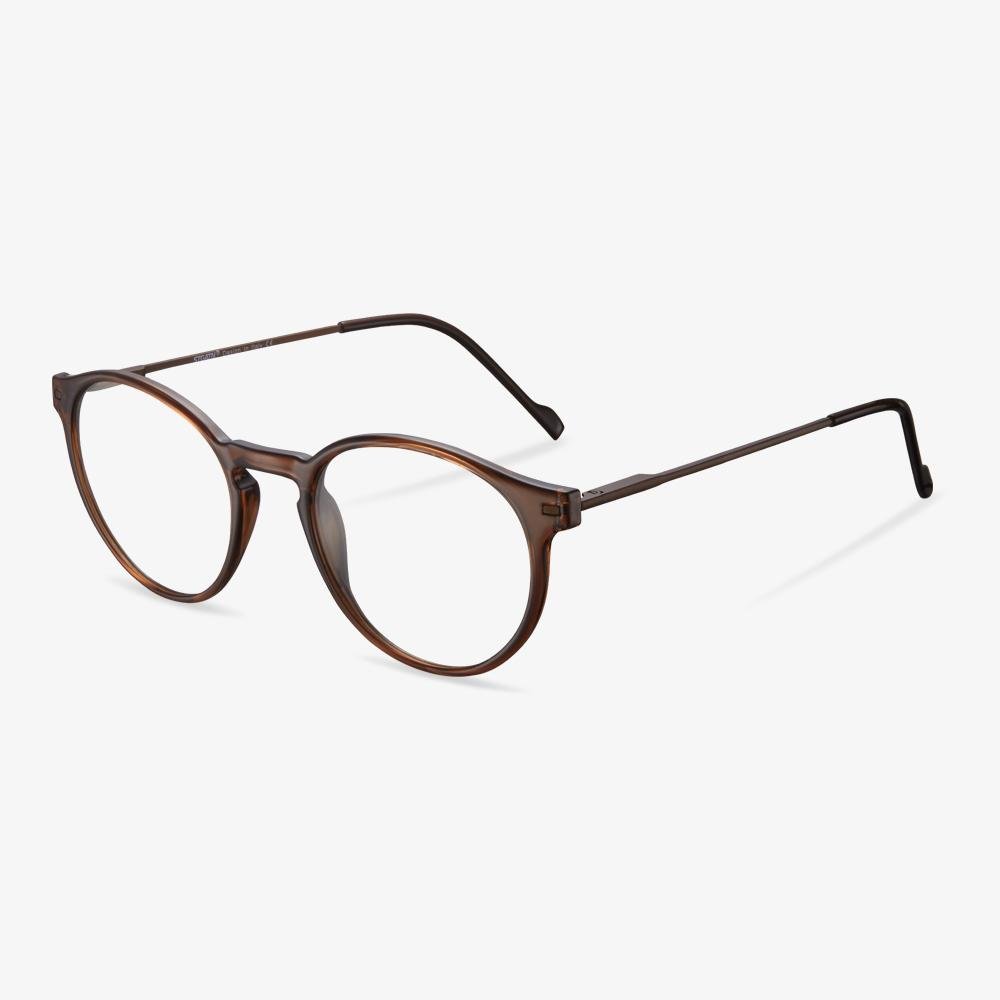
Consider the elements of frame comfort.
What we need to know is that the frame exists first as a positioning device for the lens, and secondly as a beauty. The pupil is consistent with the optical center of the lens, so it should not be too high or too low. The horizontal direction is not skewed, and there is no one high and one low phenomenon. Bilateral symmetry is a standard for manufacturing enterprises. Non-mechanical symmetry is for the wearer. The frame should be adjusted according to the size of the wearer's face. The frame is not easy to slide down, and frequent slide is prone to the phenomenon that the pupil is too high and low to match the face.
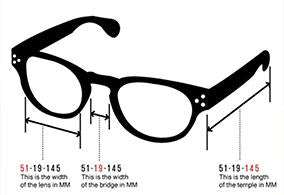
Glasses Size - Temple Length
The length of the temple is the length of the arm of your glasses. It's how far the arm is bent, all the way to where it intersects the frame. Although lengths may range from 120 to 150 mm, there are some common industry standards:135, 140, 145, and 150 mm. The temples are long enough to extend beyond your ears, so the ends can be changed to match the contours of your head behind your ears.
The Advantages of Trifocal Lenses
The greatest advantage of trifocal lenses is that they have three prescriptions in one, which means that not only do you not have to buy three separate pairs of glasses, but you also won’t have to constantly change them as you go about your day.
Another advantage of trifocal lenses is that in some cases, they offer a broader viewing area for near and intermediate-distance applications like reading and using the computer.
There are three processes for resin-changing lenses.
The incorporation method, known as bulk polymerization, is similar to the method of glass lens, that is, one or more photochromic dyes are directly incorporated into the polymer monomer of the substrate for bulk polymerization, and the lens formed after curing will change color. Discoloration dye is completely integrated into the resin lens substrate, so the lens made of color persistence is very good.
The uniformity of discoloration and the depth of color after discoloration are highly related to the thickness of the lens. Because the thickness of the lenses at all levels is different, there will be a color difference between the depth of discoloration and the uniformity, and the uneven phenomenon of high brightness is more obvious.
The film type is known as the coating method. It is the chromatic resin lens by coating or dipping in a layer of chromatic dye on the base of the resin lens. Because the coating covers the surface of the lens, the color uniformity is good. The coating, which is only about 0.05mm thick, does not provide enough molecules to make the lens dark enough, so the color is relatively less dark, and the discoloration lasts slightly longer.
Infiltration, known as the penetration method, is to use the principle of penetration, through the thermal diffusion method to make the color dye permeate the surface of the resin lens sheet material, with diffusion depth up to 0.15~0.20mm. The lens has a constant color change characteristic. There will be no inconsistency between the center and the surrounding color as the luminosity gets darker. The color-changing resin lens made by infiltration type has the benefits of uniform color-changing, small color difference, fast and thorough color-fading, which is the mainstream of color-changing technology at present.
Progressive lenses and single vision lenses
Single vision lenses are the most commonly used prescription lenses. This lens type has a single field of view or a prescription ability of the entire lens and can be used to correct myopia (nearsightedness) or hyperopia (supervision).
Progressive multifocal lenses are lenses with different upper and lower powers for the upper part to see far, and the lower part to see near. The distance from the fixed power above the lens to the fixed power below the lens does not change suddenly, but there is a gradual transition between the two through the gradual change in refractive power.
What is the cheapest way to buy prescription glasses?
Optometry must be accurate. Optometry is the main basis for glasses. The accuracy of optometry is directly related to the success rate of the glasses prepared. Optometry must be accurate first, and the difference between the upper and lower levels should not exceed 12.5 degrees of the prescription. Secondly, the astigmatism axis should be accurate, and the general axis difference should be limited to plus or minus l to 3 degrees. In addition, the interpupillary distance must be accurate, and the interpupillary distance must be equal to the optical center distance of the lens. If you do not pay attention to the above-mentioned checkpoints in optometry, the prepared spectacle lenses will have blurred vision, prolonged visual fatigue, dizziness, nausea, and even diplopia. Optometry is best to go to a professional eye hospital. For children’s optometry or to wear glasses for the first time, you must use mydriatic optometry to be accurate. You can also check if there is any problem with the fundus, and go to the hospital to get more accurate optometry.
How to Adjust Crooked Glasses
If one side of your frame looks higher than the other, you need to adjust the arms of your glasses. So, how to adjust glasses?
If the right side is higher than the left, you need to gently bend the left arm down at the hinge or where the arm bends behind your ear. If the left side is higher than the left, so just do the same action on the opposite side.
When adjusting crooked glasses, you need to adjust frames a little bit at a time to avoid overcompensating and possibly damaging your glasses. You can run the arms under the warm water but do not running the warm water over the lenses because it will affect the lens coating.